How to Install Postman on Ubuntu 24.04
In this guide, we will explore how to install Postman on Ubuntu 22.04. Whether you're a beginner or already familiar with Postman, you'll find helpful instructions here. It covers what Postman is, its key benefits, common use cases, and step-by-step instructions for installing it on your system.
What is Postman?
Postman is a widely used tool designed to simplify working with APIs. It’s a handy tool for developers, testers, and anyone creating or using APIs. With its easy-to-use interface, Postman makes it convenient to build, test, and document APIs effectively.
It works across major operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, and also offers a browser-based version for those who prefer not to install software. The free version of Postman provides enough features for most individual or small team needs. The paid Pro version is also available for more advanced functionality and team-based collaboration.
What are the Practical Uses of Postman in API Development?
Postman is a versatile tool that helps developers and testers manage and work with APIs efficiently. Here are five common ways Postman is used:
Manual API Testing
Postman is widely used for sending different types of HTTP requests, such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, to check how APIs respond. Developers can set request headers, body content (like JSON or form data), and query parameters. The response can be reviewed in detail, including status codes and headers, to confirm the API works as expected under various scenarios.
Automated API Testing
Postman allows users to write scripts using JavaScript to automate testing. These scripts can verify if the response status code is correct, check the structure of the returned JSON, and validate specific values. These automated tests can be grouped into collections and run using tools like Collection Runner or integrated into CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing.
Developing and Debugging APIs
Backend developers use Postman during API development to quickly test endpoints as they build them. Postman makes it easy to send test requests to local or test servers,examine the responses, and troubleshoot errors. It also supports environment variables, which makes switching between local, testing, and staging environments simple.
Creating API Documentation
Postman can generate documentation automatically from collections. Developers can add explanations, sample requests, and response examples to each API endpoint. The resulting documentation is interactive and can be shared with frontend teams or third-party developers to help them integrate more easily.
Monitoring API Performance
Postman provides monitoring features that allow scheduled testing of API endpoints. These monitors run collections at specific times and notify teams if something goes wrong, such as a failed test or a slow response. Alerts can be sent via email or tools like Slack to help teams respond quickly to issues in production.
Postman also integrates with tools like GitHub, Jenkins, and Newman, and supports many plugins and extensions, allowing teams to extend its capabilities and fit it into their development workflows.
Prerequisites
Before getting started with the Postman installation on Ubuntu 24.04, make sure the following requirements are met:
- A system running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A user account with permission to install software.
- An active internet connection for downloading and testing Postman.
How to install Postman on Ubuntu 24.04?
There are a couple of easy ways to install Postman on Ubuntu. This guide will walk you through both options, so you can choose the method that fits your preference.
Update Your System
Before installing any new application, it's a good practice to update your system packages. This ensures that all dependencies are up to date and helps new software run smoothly.
To update your package list, run:
$ sudo apt updateMethod 1: Install Postman on Ubuntu Using Snap
Snap is a package management system created by Canonical, the makers of Ubuntu. It simplifies software installation and management. Most modern versions of Ubuntu come with Snap pre-installed.
To install Postman on Ubuntu using Snap, use this command:
$ sudo snap install postman
If Snap is not already installed, you can install it with:
$ sudo apt install snapdOnce installed, Snap allows you to easily manage and update Postman and many other applications.
![]()
Method 2: Install Postman on Ubuntu via Flathub (Flatpak)
Flathub is a widely used platform for distributing Flatpak applications. Flatpak is a universal packaging system that allows developers to bundle software along with its dependencies, making installations easier and more consistent across different Linux distributions.
Step 1: Install Flatpak
If Flatpak is not already installed on your system, you can add it by running:
$ sudo apt install flatpakThis installs the Flatpak framework needed to run apps from Flathub.
Step 2: Add the Flathub Repository
Flathub is the central source for most Flatpak applications, including Postman. To connect your system to Flathub, use:
$ flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThis ensures you have access to all the applications hosted on Flathub.
Step 3: Install Postman on Ubuntu Using Flatpak
Now, you can install Postman directly from Flathub by executing:
$ flatpak install flathub com.getpostman.Postman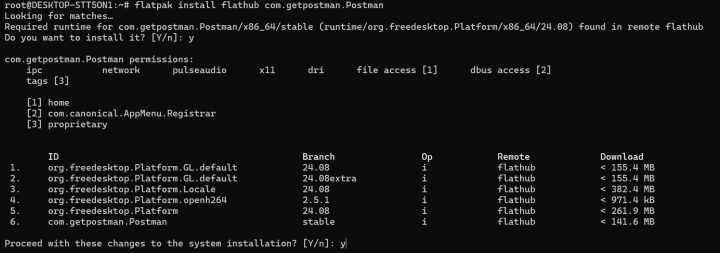
This command will download and install the latest Postman package available on Flathub.
Step 4: Launching Postman
Once installed, you can start Postman by typing the following command in the terminal:
$ flatpak run com.getpostman.PostmanAlternatively, you can open it from the application launcher by simply searching for "Postman."
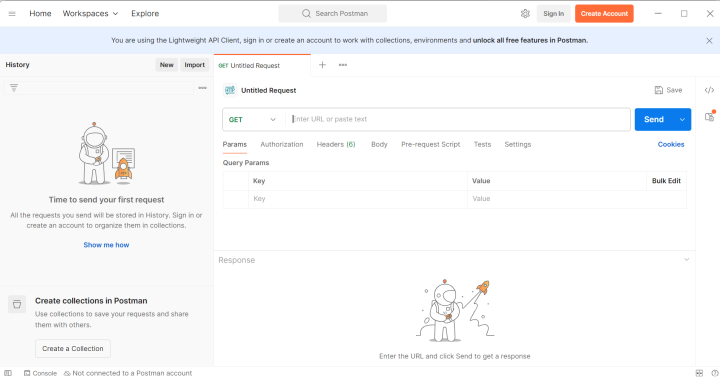
How to Use Postman? (Getting Started with Postman)
If you’re new to Postman, the best way to learn is to open the app and start exploring its layout and tools. Here are some basic steps and tips to help you become familiar with Postman's environment.
Postman Interface
Once you launch Postman, take some time to explore its main components:
- Request Builder: This is where you create and configure API requests.
- Response Viewer: Here, you can view the results returned by the API.
- Sidebar: Helps you navigate between different collections, environments, and history.
Send a Basic GET Request
To test how it works, try sending a simple GET request:
- Enter a public API URL into the request input field.
- Set the HTTP method to GET.
- Click the Send button.
The API’s response will appear in the response viewer, where you can inspect status codes, response data, and headers.
HTTP Methods
Once you’ve mastered GET requests, try experimenting with other common HTTP methods like:
- POST – for creating new resources
- PUT – for updating existing data
- DELETE – for removing resources
Each method can be selected from the dropdown in the request builder.
How to Remove Postman from Ubuntu? (Uninstall Postman)
If you no longer need Postman on your Ubuntu system, you can uninstall it using the same method you used for installation.
Method 1: Uninstall Postman via Snap
If Postman was installed using Snap, run this command to remove it:
$ sudo snap remove postman
Method 2: Uninstall Postman via Flatpak (Flathub)
If you used Flatpak through Flathub, use the following command:
$ flatpak uninstall flathub com.getpostman.PostmanConclusion
In the above tutorial, we demonstrated how to install and uninstall Postman using both Snap and Flatpak. There's no strict rule on which method to use—just choose the one you're most comfortable with or that offers the latest version of the app.
Experience the power of a Virtual Private Server with the flexibility and reliability of cloud technology at BlueVPS. Enjoy a dedicated environment tailored to your needs—fully customizable, easily scalable, and built for performance. With unlimited traffic and full control over your resources, it’s the perfect solution for businesses and developers alike.
Blog